What Is a TVSS? Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors
14 April 2023
Share this article:

What is a TVSS Device?
A TVSS is a device that cuts off the power from the AC line when encountering a power surge or a power spike, which are considered transients. The name TVSS has officially been replaced with the more commonly known phrase surge power device (SPD) yet is still in use today. The devices cut off the flow of power when there is a surge or spike to prevent sensitive and critical-mission equipment from becoming damaged. These devices differ from uninterruptible power supply (UPS) devices as TVSS devices do not store energy in a backup battery pack for later use due to a power outage.
Power system transients occur for a short period of time at very high voltages. A common type of transient would be considered a lightning strike. The surge can happen within a microsecond (1/1000 second) or millisecond (1/1000000 second). A transient voltage surge suppressor is designed to offer some protection from these transients yet cannot always handle large overvoltages such as 50,000v that can come from a lightning strike.
What Does a Transient Voltage Surge Suppressor Do?
A transient voltage surge suppressor monitors the voltage from the AC power line. It takes into account the input and output waveforms and does nothing during normal power operating functions. When detecting an abnormality in the voltage, the TVSS closes its switch. This process prevents the surge or spike from traveling further up the line and into the connected devices. TVSSs are commonly used to protect sensitive electronic equipment from damage caused by voltage spikes and surges, such as those that can occur during lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations.
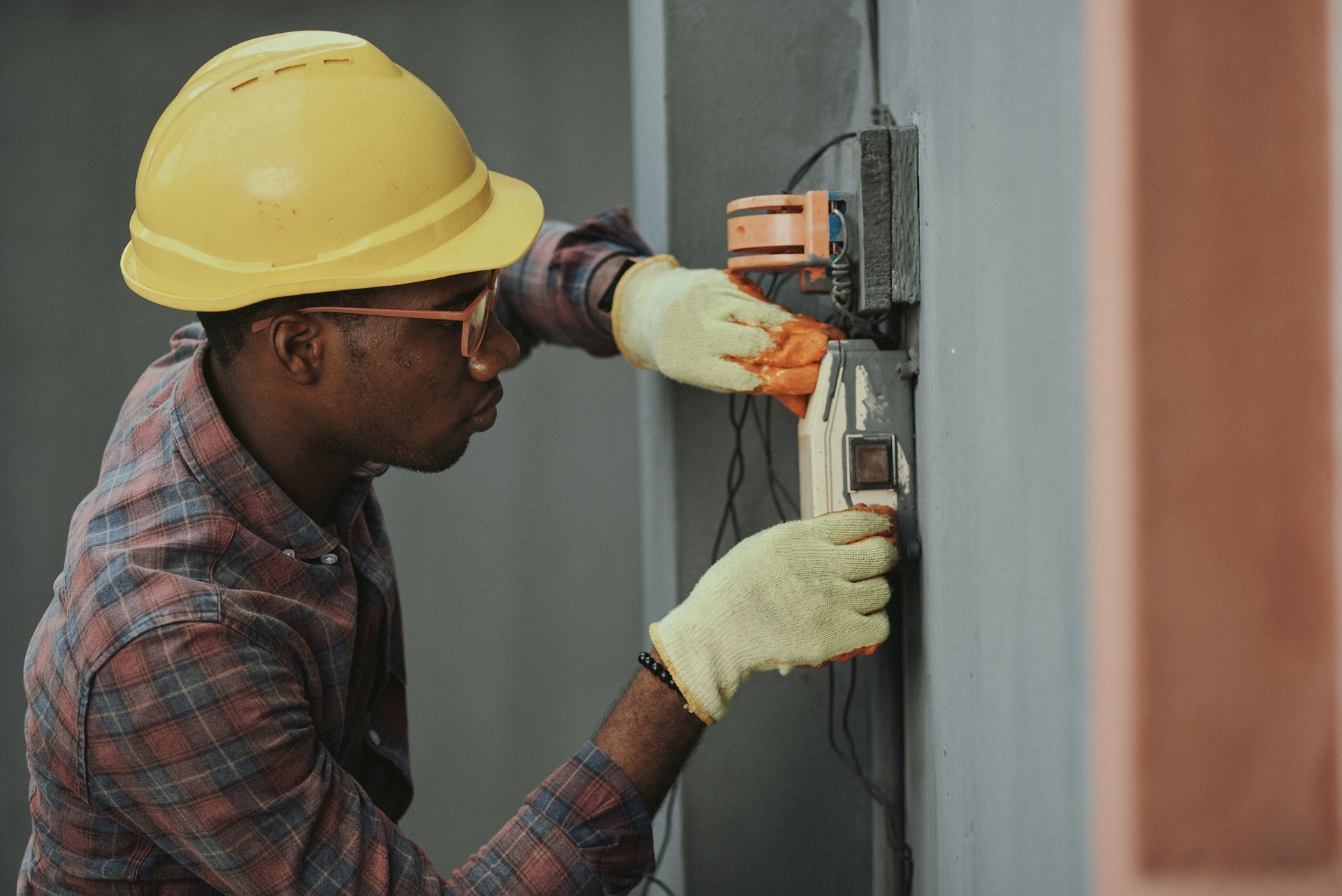

Types of TVSS
When looking at TVSS and other surge protection equipment, you will notice that there are different types of these devices. Each TVSS device is categorized by type (1, 2, or 3) or by category (A, B, or C) based on where it is installed along the AC line. Understanding where they are installed and what functions are included in the device.
Type 1 (Category C) TVSS:
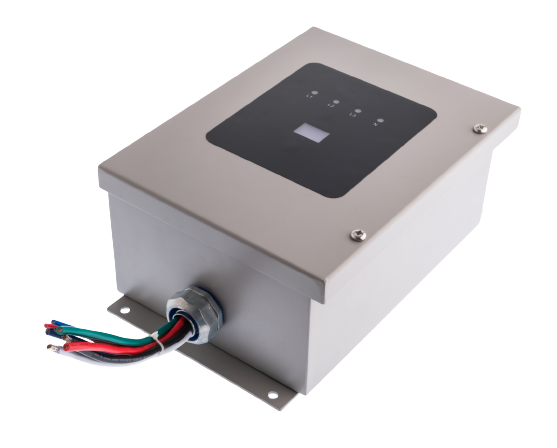

These devices are installed along the line side of the device yet can be placed in any location in the power distribution system. So you may find a Type 1 TVSS outside the service entrance, inside the building along the branch panel, or up to the point of use for the connected device. The device will have different functions such as overcurrent protection installed. It does not require external overcurrent protection. The Type 1 TVSS has a nominal discharge current of 10kA or 20kA. The Type 1 TVSS is designed to handle high-energy surges and is suitable for use in applications where lightning protection is required.
Type 2 (Category B) TVSS:
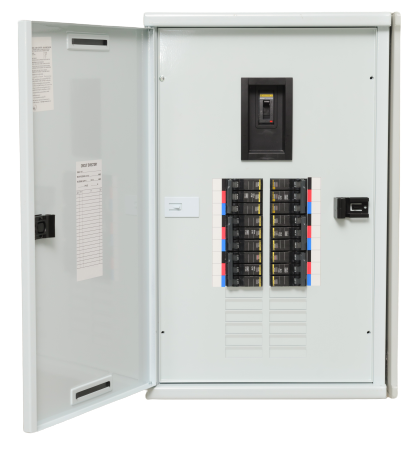

You will install a Type 2 TVSS at the load side to the service entrance. The load side is considered the service entrance for the AC power line at the branch panel. Some TVSS have overcurrent protection while others will require external overcurrent protection from other devices such as a CB or fuse). The nominal discharge current for Type 2 TVSS is 3kA, 5kA, 10kA, or 20kA. The Type 2 TVSS is typically used to protect individual devices or equipment within a facility from the effects of smaller, more frequent voltage surges and spikes. These devices are commonly found in commercial and industrial settings, where the cost of equipment damage due to electrical disturbances can be high.
Type 3 (Category A) TVSS:
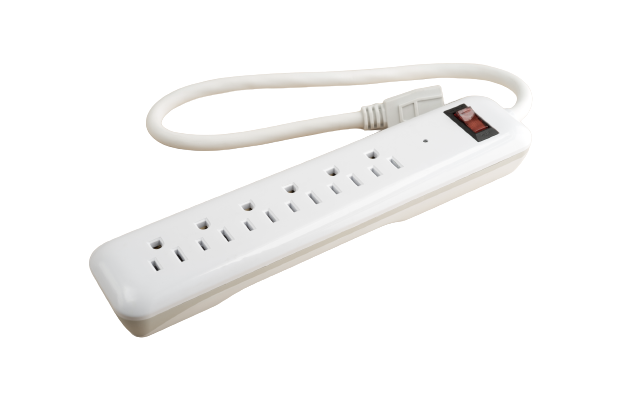

The Type 3 TVSS are devices such as receptacles, plugs, or power strips, which become installed near the connected electronic device that it is protecting. These devices are very common for both commercial offices and residential homes to protect smaller electronics from surges that may come from wall outlets.
Keep in mind that Type 1 and Type 2 TVSS are hardwired into the AC line while the Type 3 TVSS are considered plug-ins. In addition to certain TVSS identified by category or type, other TVSS may be defined by the design of the switch components and how much voltage they can handle. They are also categorized by their response time. There are three types called clamps, crowbars, and hybrids.
When selecting a TVSS, you want to understand the power surges that may commonly occur in your building or region. You also want to look for a UL listing on the device that says TVSS. If the device does not have this listing or says "TAP" on the label, it may be a current tap device that looks like a TVSS but does not have a protection value. Ensure the hard-wired TVSS that you purchase comes with a component schematic for maintenance and servicing, and that the TVSS comes with a warranty.
When you are in need of surge suppressor devices, surge protection devices, UPS systems, and other backup power supply systems, turn to the experts at Facility Gateway Corporation. Contact us today to learn more.
Connect with Us: