DC Power Systems Overview - The Role of the UPS
29 December 2021
Share this article:
What is DC Power?
Direct current (DC) is the one-directional flow of electricity. As opposed to alternating current (AC), DC electric current flows in a constant direction. AC power is converted from DC power through rectifiers, which only allow electric currents to flow in one direction. DC power is converted into AC power through an inverter, which uses electronic components like inductors and capacitors or transformers. These tools can’t give out more power than they take in, and during the process of switching AC to DC or DC to AC power, some energy is lost in the process and becomes heat.
DC power is used in a range of applications, from household uses like flashlights and remotes, to charging batteries, to the provision of electric supply for industrial motors and railways. In high-voltage form, DC power is even used to transmit huge amounts of electricity from remote generators and to connect power grids.
Read more for an overview on DC power systems, including the role of DC power UPS plays and the main components of the system.
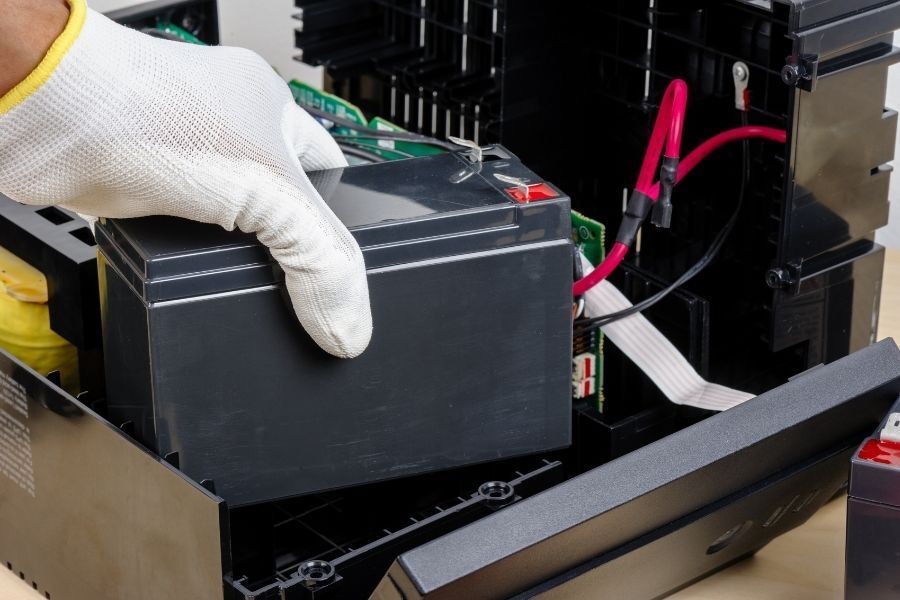

What is the Role of DC Power in a UPS?
DC Power is very commonly used in emergency power situations, through the use of UPS (uninterruptible power supply) systems. A UPS system is an electrical apparatus that provides emergency power to a load when the input power source or mains power fails. Businesses everywhere rely on UPS systems to power their electronic equipment in the event of an unexpected power outage.
Electricity blackouts, spikes, surges, or over-voltage could typically mean the loss of critical data, and perhaps millions of dollars in damage and lost profits. UPS systems keep the lights on so companies can function as normal until normal power resumes. UPS systems can be small, protecting a single computer, to large, protecting entire companies, data centers, schools, factories, and hospitals.
Though some are mechanical in nature, most UPS systems store electricity in a series of rechargeable batteries. When normal power is on, or in other words-when not experiencing a power outage-the batteries of the UPS system are charged by DC power. In most situations and applications, this DC power is then converted from AC power through the use of a transformer and rectifier circuit.
When an unexpected power outage occurs, the pre-charged batteries of the UPS system are full of DC power. Most equipment requires AC power to run, however. In a “typical” UPS system, the UPS system’s inverter converts the DC power back to AC power again, so your normal functions can resume.
What is a DC Power System?
A DC power system is a UPS system that provides DC output in the same uninterruptible manner any UPS system could. This system provides DC power to equipment and is used in a range of industries. As previously described, most equipment operates using AC power, but when long discharge and low amperage output is required, DC systems are preferred. DC systems typically convert AC to DC power when an electricity blackout occurs. They also keep backup batteries charged and regulate the electricity sent to your equipment, so you use the correct input voltage.
What are the Main Components of a DC Power System?
There are five main components of a DC Power System. Briefly described below, they are:
The rectifier/charger: This is an electrical device converting AC to DC power. Not only does it provide DC power, but it also charges backup batteries. The rectifier/charger is the hero of the system, and it’s what makes sure the system can continue to work when an unexpected electricity blackout occurs.
The controller: The controller is the component of a DC system that sends instructions to the other components within the system using communication protocols.
The batteries: Different DC power systems can use different kinds of batteries. Some of the most common types of batteries a DC system may use are VLRA batteries, wet cell batteries, lithium-ion batteries, or NICAD batteries. What type of battery a DC power system uses will depend on the specific application, and several other considerations, including the temperature within the building where the system is stored, available budget, and environmental concerns, among other things.
The distribution system: The distribution system is the part of the system that provides electricity for ultimate use. The distribution system may be external, or it may not be housed in the same area as the rectifier, but it is a separate component within the DC system.
The enclosure: There are so many different types of DC power system enclosures, and many are environment and/or application specific. Common enclosure designs include shelf mount and rack mount enclosures.
Need DC System / UPS Assistance or Advice?
Facility Gateway Corporation understands the importance of selecting the right UPS to protect your business in the event of an unexpected power outage, and we also know how crucial it is to provide proper UPS maintenance. At FGC, we are happy to provide advice, UPS maintenance, or set your business up with the right UPS system to fit your unique needs.
To speak with one of our UPS system experts directly, contact Facility Gateway Corporation at any time at866-255-6030 for emergency UPS & battery service needs, or call our U.S. based National Operating Center at 866-432-1711. We also invite you to contact us via our online contact form, or start a chat with our team in the chat feature at the bottom right corner of this page! Let us be your partner for uninterruptible power supply services.
Connect with Us: